HOW TO CONFIGURE SLAVE DNS SERVER WITH BIND ( SECONDARY DNS SERVER ) IN LINUX
CONFIGURE SLAVE DNS SERVER WITH BIND ( SECONDARY DNS SERVER ) IN LINUX
Today in this article we are going to discuss How to Configure Slave/Secondary DNS Server in Linux. Slave DNS Server is also referred as Secondary DNS Server. In my previous article I explained How to Setup a Master/Primary DNS Server with BIND, Please Read the Master/Primary DNS Server Configuration article before read this article so that you can properly understand the whole topic.
Introduction
Slave/Secondary DNS Server is a server which is like a Load balancer or Backup server of Master/Primary DNS Server, Its takes all DNS query Records/Zones from Master Server. As Slave/Secondary DNS Server is a exact copy of the master DNS server, In case the Master/Primary Server becomes unavailable or server got down due to some reason, till the server gets up the Secondary DNS Server will accept the query without effecting the end user work.
Follow the Below Steps to Configure Slave/Secondary DNS Server
Step: 1 Configure from Master Server End
Before configure the Slave/Secondary DNS Server we need to do some changes in our all Master/Primary DNS Server configuration files i.e. named.conf ( Main Configuration File ), elinuxbook.com.for ( Forward Zone ), elinuxbook.com.rev ( Reverse Zone ) to allow the Query and Zone record transfer to Slave Server.
First configure the /etc/named.conf
Let’s go ahead and configure the /etc/named.conf in Master Server. All changes are highlighted in Blue Color.
//
// named.conf
//
// Provided by Red Hat bind package to configure the ISC BIND named(8) DNS
// server as a caching only nameserver (as a localhost DNS resolver only).
//
// See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files.
//
options {
listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; 192.168.1.100; };
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
allow-query { localhost; 192.168.1.0/24; };
allow-transfer { 192.168.1.101; };
recursion yes;
dnssec-enable yes;
dnssec-validation yes;
/* Path to ISC DLV key */
bindkeys-file "/etc/named.iscdlv.key";
managed-keys-directory "/var/named/dynamic";
};
logging {
channel default_debug {
file "data/named.run";
severity dynamic;
};
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
include "/etc/named.root.key";
### ELinuxBook Internal Zones ###
### Forward Zone ###
zone "elinuxbook.com" IN { # Domain Name
type master;
file "elinuxbook.com.for"; # Name of the Forward Zone File
allow-update { none; };
allow-transfer { 192.168.1.101; };
};
### Reverse Zone ###
zone "1.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN { # IP Address
type master;
file "elinuxbook.com.rev"; # Name of the Reverse Zone File
allow-update { none; };
allow-transfer { 192.168.1.101; };
};
We have done all required changes, now run the below command to check if all syntax are correctly written or not.
[root@ns1 ~]# named-checkconf /etc/named.conf
Configure the Forward Zone
Now configure the Forward Zone in Master Server in my case it’s elinuxbook.com.for, All changes are Highlighted in blue Color.
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA ns1.elinuxbook.com. root@ns1.elinuxbook.com. (
2010031403 ; serial
3600 ; refresh
1800 ; retry
604800 ; expire
86400 ) ; minimum
; name servers
@ IN NS ns1.elinuxbook.com.
@ IN NS ns2.elinuxbook.com.
; name server A records
ns1 IN A 192.168.1.100
ns2 IN A 192.168.1.101
elinuxbook.com. IN A 192.168.1.100
; mail exchanger record (MX record)
IN MX 5 ns1.elinuxbook.com.
; host and canonical name records
mail IN CNAME ns1.elinuxbook.com.
www IN A 192.168.1.100
ftp IN A 192.168.1.100
Configure the Reverse Zone
Now configure the Reverse Zone in Master Server in my case it’s elinuxbook.com.rev, All changes are Highlighted in blue Color.
TTL 86400
@ IN SOA ns1.elinuxbook.com. root@ns1.elinuxbook.com (
2010031402 ; serial
28800 ; refresh
14400 ; retry
3600000 ; expire
86400 ) ; minimum
; name servers
IN NS ns1.elinuxbook.com.
IN NS ns2.elinuxbook.com.
; name server A records
ns1 IN A 192.168.1.100
ns2 IN A 192.168.1.101
; PTR records
100 IN PTR ns1.elinuxbook.com.
101 IN PTR ns2.elinuxbook.com.
After all required changes in Forward and Reverse in Master/primary DNS Server just run the below command to check if all syntax are properly written or not.
[root@ns1 ~]# named-checkzone elinuxbook.com /var/named/elinuxbook.com.for zone elinuxbook.com/IN: loaded serial 2010031403 OK [root@ns1 ~]# named-checkzone elinuxbook.com /var/named/elinuxbook.com.rev zone elinuxbook.com/IN: loaded serial 2010031402 OK
Then restart the named service by below command to take effect.
[root@ns1 ~]# /etc/init.d/named restart Stopping named: . [ OK ] Starting named: [ OK ]
Step: 2 Configure from Slave Server End
My Scenario :
- IP Address : 192.168.1.101
- Domain Name : elinuxbook.com
- Hostname : ns2
- FQDN ( Fully Qualified Domain Name ) : ns2.elinuxbook.com
Before we start the configuration we need to prepare our system and do some configuration, So follow the below steps :
Configure the Network Card
First we need to configure the network card and assign IP Address, Subnet Mask to our System.
So edit the Network card ( In my case it’s eth1 ) , using nano editor as shown below.
[root@localhost ~]# nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
DEVICE=eth1 BOOTPROTO=none IPADDR=192.168.1.101 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 DOMAIN=elinuxbook.com DNS1=192.168.1.100 HWADDR=00:0c:29:90:78:32 IPV6INIT=yes NM_CONTROLLED=yes ONBOOT=yes TYPE=Ethernet UUID="5d8d8030-3bf2-4487-8a98-400dc314480f" USERCTL=no PEERDNS=yes
Change the Computer Name
Follow the below step to Change the Computer Name. ( Make Changes as shown below Highlighted in Blue Color).
[root@localhost ~]# nano /etc/sysconfig/network
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=ns2.elinuxbook.com
Configure the /etc/resolv.conf
After update the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1 file the /etc/resolv.conf file would look like this as shown below.
[root@localhost ~]# nano /etc/resolv.conf
Generated by NetworkManager search elinuxbook.com nameserver 192.168.1.100
Configure the hosts File ( /etc/hosts )
Update the host file as shown below (Highlighted in Blue Color).
[root@ns2 ~]# nano /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.1.101 ns2 ns2.elinuxbook.com
Install Required Packages
Let’s go ahead and install required packages of bind, We need to install below packages to configure Slave/Secondary DNS Server.
- bind
- bind-utils
- bind-libs
Follow the below command to install the same.
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install bind
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Setting up Install Process
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: centos.excellmedia.net
* extras: centos.excellmedia.net
* updates: centos.excellmedia.net
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package bind.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: bind-libs = 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 for package: 32:bind-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package bind-libs.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6 will be updated
--> Processing Dependency: bind-libs = 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6 for package: 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64
---> Package bind-libs.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 will be an update
--> Running transaction check
---> Package bind-utils.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6 will be updated
---> Package bind-utils.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 will be an update
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
bind x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 updates 4.0 M
Updating for dependencies:
bind-libs x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 updates 890 k
bind-utils x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 updates 187 k
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 1 Package(s)
Upgrade 2 Package(s)
Total download size: 5.0 M
Downloading Packages:
(1/3): bind-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64.rpm | 4.0 MB 00:29
(2/3): bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64.rpm | 890 kB 00:07
(3/3): bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64.rpm | 187 kB 00:02
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 130 kB/s | 5.0 MB 00:39
Running rpm_check_debug
Running Transaction Test
Transaction Test Succeeded
Running Transaction
Updating : 32:bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 1/5
Updating : 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 2/5
Installing : 32:bind-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 3/5
Cleanup : 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64 4/5
Cleanup : 32:bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64 5/5
Verifying : 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 1/5
Verifying : 32:bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 2/5
Verifying : 32:bind-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 3/5
Verifying : 32:bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64 4/5
Verifying : 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64 5/5
Installed:
bind.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3
Dependency Updated:
bind-libs.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 bind-utils.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3
Complete!
Configure the Main Configuration File (/etc/named.conf)
we have installed all required Packages, Now we need to configure the main configuration file of Slave/Secondary DNS Server i.e. named.conf to create Forward and Reverse Zones from Slave server end to replicate with Master Server, So follow the below steps to do the same.
Here below I have mentioned my named.conf file and Highlighted all required changes I did in Blue Color.
//
// named.conf
//
// Provided by Red Hat bind package to configure the ISC BIND named(8) DNS
// server as a caching only nameserver (as a localhost DNS resolver only).
//
// See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files.
//
options {
listen-on port 53 { any; };
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
allow-query { any; };
recursion yes;
dnssec-enable yes;
dnssec-validation yes;
/* Path to ISC DLV key */
bindkeys-file "/etc/named.iscdlv.key";
managed-keys-directory "/var/named/dynamic";
};
logging {
channel default_debug {
file "data/named.run";
severity dynamic;
};
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
include "/etc/named.root.key";
### Internal DNS Slave Zones ###
zone "elinuxbook.com" IN {
type slave;
masters { 192.168.1.100; };
file "slaves/elinuxbook.com.for";
};
zone "1.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type slave;
masters { 192.168.1.100; };
file "slaves/elinuxbook.com.rev";
};
We have done all required changes, now run the below command to check if all syntax are correctly written or not.
[root@ns2 ~]# named-checkconf /etc/named.conf
Now start the DNS Server by below command.
[root@ns2 ~]# /etc/init.d/named start Starting named: [ OK ]
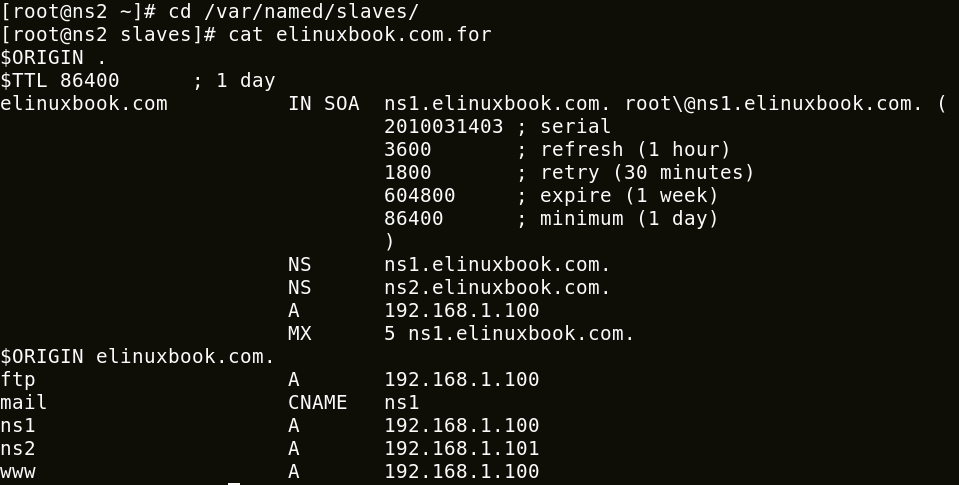
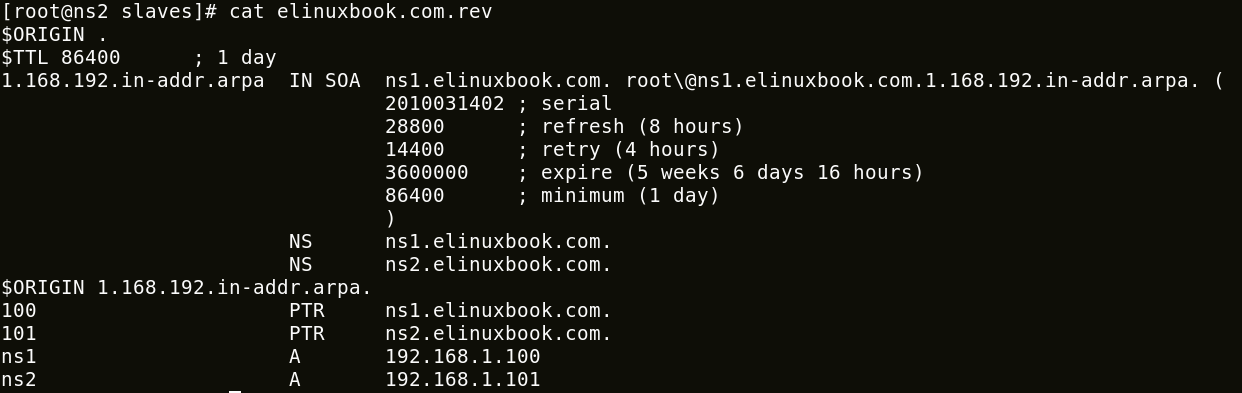
After start the DNS service the zone files will automatically created in /var/named/slaves.
[root@ns2 ~]# cd /var/named/slaves/ [root@ns2 slaves]# ls -l total 8 -rw-r--r--. 1 named named 494 Jan 8 09:30 elinuxbook.com.for -rw-r--r--. 1 named named 499 Jan 8 09:30 elinuxbook.com.rev
Snapshots are shown below :
1. Forward Lookup Zone
2. Reverse Lookup Zone
Now start the DNS service on startup using below command.
[root@ns2 ~]# chkconfig --level 35 named on [root@ns2 ~]# chkconfig --list named named 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:off 5:on 6:off
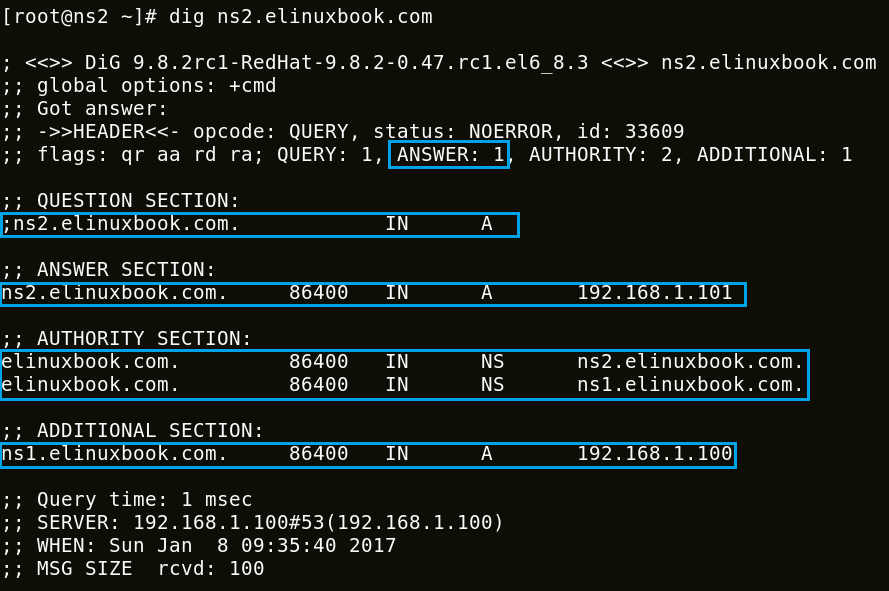
So we have successfully configured the BIND DNS Service, Now it’s time for testing., We have tools like dig, nslookup to check the DNS service working status. So the Command would look like as mentioned below.
dig <FQDN ( Fully Qualified Domain Name/IP Address )> i.e. dig ns1.elinuxbook.com
Check from Slave Server end as shown below.
We can check by using nslookup command as shown below.
[root@ns1 ~]# nslookup elinuxbook.com Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Name: elinuxbook.com Address: 192.168.1.100 [root@ns1 ~]# nslookup ns1.elinuxbook.com Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Name: ns1.elinuxbook.com Address: 192.168.1.100 [root@ns1 ~]# nslookup ns2.elinuxbook.com Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Name: ns2.elinuxbook.com Address: 192.168.1.101 [root@ns1 ~]# nslookup 192.168.1.100 Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 100.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa name = ns1.elinuxbook.com. [root@ns1 ~]# nslookup 192.168.1.101 Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 101.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa name = ns2.elinuxbook.com.
So everything looks good and Slave/Secondary DNS Server is working fine as shown on the testing output’s above.
If you found this Article useful then Like it, Share it, Subscribe our Site for more Linux Tutorials OR If you have any thing to say then feel free to Comment on Comment Box below.